Flood zone maps are indispensable tools for investors assessing real estate in flood-prone areas. These maps categorize zones as low, moderate, or high risk using historical data, topographical features, and water bodies. Lenders require them for loan applications, with colors indicating risk levels. Accurate mapping software overlays data, aiding in strategic investment choices, infrastructure improvements, and regulatory compliance. Historical flood events provide crucial context, especially with climate change's impact on water resources. Investors must review maps and regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure financial protection.
In the realm of real estate investment, understanding flood risks is not a mere nicety but a crucial component for informed decision-making. With climate change exacerbating weather events, investors must navigate the complexities of flood zones to mitigate potential losses and capitalize on opportunities. This article provides a detailed breakdown of flood zone maps, offering valuable insights for savvy investors. We demystify these critical tools, enabling you to assess risks accurately and make strategic choices in an ever-changing landscape. By the end, investors will be equipped with the knowledge to navigate flood zones confidently.
Understanding Flood Zone Maps: A Key Tool for Investors
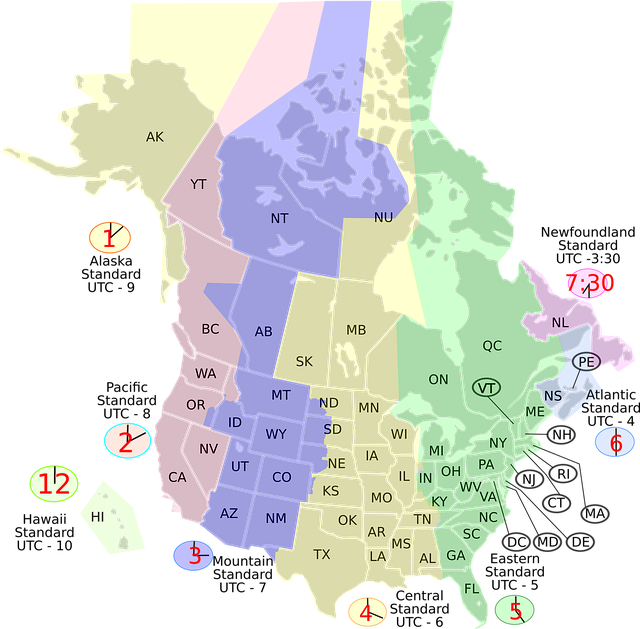
Flood zone maps are indispensable tools for investors navigating real estate markets, especially in areas prone to flooding. These detailed geographic representations illustrate regions at risk of inundation during heavy rainfall or storm surges, providing critical insights into potential property investments. Understanding the nuances of a flood zone map is essential for making informed decisions and mitigating financial risks associated with these zones.
Investors should approach these maps as more than just visual aids; they are data-driven resources that offer valuable context about local hazards. For instance, a comprehensive flood zone map might categorize areas into different risk levels—low, moderate, or high—based on historical flooding data and topographical features. By familiarizing themselves with these classifications, investors can identify properties in safer zones, reducing the likelihood of substantial financial losses due to flooding. Moreover, many lenders and mortgage providers require borrowers to conduct thorough research using flood zone maps as part of their loan application process. This requirement ensures that both parties are aware of potential risks before finalizing any transactions.
When assessing a property’s risk, investors should scrutinize various factors depicted on the map, such as floodplains, water bodies, and elevation data. For coastal areas, understanding the impact of storm surges is paramount, whereas inland regions may face risks from riverine or flash flooding events. In some cases, regulatory bodies mandate specific building codes and infrastructure improvements in high-risk zones to enhance resilience against floods. Being aware of these requirements can influence investment strategies, as investors might choose to renovate or retrofit properties to meet safer standards.
In conclusion, flood zone maps empower investors with essential knowledge, enabling them to make calculated choices in volatile real estate markets. By understanding the map’s intricacies and integrating it into their analysis, investors can navigate potential risks effectively and contribute to more sustainable and secure communities.
Identifying High-Risk Areas: Analyzing Geographical Data

Identifying high-risk areas is a critical component of responsible investing, especially when considering properties located within flood zones. A detailed examination of geographical data allows investors to navigate these risks effectively. Flood zone maps, integral tools in this process, provide a visual representation of areas prone to flooding, enabling borrowers and lenders alike to make informed decisions.
Geographical analysis involves scrutinizing various factors such as topography, water bodies, historical flood events, and climate patterns. For instance, properties near rivers, lakes, or coastal regions are more susceptible to flooding compared to elevated terrain. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), nearly 14 million people in the United States live in high-risk flood zones. Understanding these patterns is essential for investors to assess a property’s long-term viability and potential insurance requirements.
The process of analyzing geographical data includes accessing comprehensive datasets, employing geospatial analysis tools, and interpreting results accurately. Advanced mapping software can overlay multiple layers of information, such as elevation models, land use data, and historical floodplain boundaries, to create detailed flood zone maps. These maps are updated regularly to account for changes in terrain and environmental conditions, ensuring borrowers have access to the most current risk assessments.
By integrating geographical insights into investment strategies, investors can mitigate potential losses associated with flooding. This proactive approach allows them to make informed choices, especially when considering property acquisition or refinancing, where understanding borrower requirements for flood zone maps is paramount. It enables lenders to evaluate risks accurately and implement appropriate measures, ensuring both the safety of investments and compliance with regulatory standards.
Interpreting Map Layers: Demystifying Symbols and Colors
When examining a flood zone map for investment purposes, understanding its layers is crucial. Each layer represents distinct data points like regulatory zones, elevation levels, or historical flooding events. Symbols and colors play a vital role here; they provide visual cues about risks associated with different areas. For instance, red typically signifies high-risk flood zones, while yellow might indicate moderate risk. Green often denotes areas outside these zones.
Let’s consider an example: in a recent update, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) introduced digital mapping tools offering detailed 3D visualizations. These maps allow investors to explore various layers, such as the 100-year flood zone, which helps assess potential risks. Borrowers looking for financing should be aware of these map updates, as they can impact loan eligibility and interest rates, especially in high-risk areas. The flood zone map borrower requirements may vary based on these insights.
Interpretation demands a nuanced approach. Some symbols represent specific hazards like river floodplains or coastal zones prone to storm surges. Elevation data is also critical; higher elevations generally pose lower risks. Investors should cross-reference these layers with historical data to gain accurate pictures of potential outcomes. By doing so, they can make informed decisions and mitigate risks effectively.
Remember, a comprehensive understanding of the flood zone map empowers investors to navigate real estate markets more strategically. It’s not just about avoiding red zones; it’s about discerning all factors that influence risk assessment. This meticulous analysis becomes increasingly vital as climate change patterns impact water resources globally. Staying informed about these changes and their implications on flood zone maps is essential for both borrowers and lenders alike.
Historical Flood Events: Learning from Past Patterns
Historical Flood Events play a critical role in understanding and interpreting flood zone maps for investors. By studying past patterns, we gain valuable insights into the frequency, intensity, and potential impact of future flooding events. Data from historical records reveals that many regions prone to floods exhibit recurring patterns, often linked to specific seasons, weather conditions, or geographic features. For instance, coastal areas in Texas have experienced significant flood events during intense hurricane seasons, while riverine communities along the Mississippi River are accustomed to seasonal overflows.
Analyzing these historical trends is essential for creating accurate flood zone maps that reflect current and future risk levels. These maps serve as critical tools for lenders and borrowers alike, guiding investment decisions and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. For example, a flood zone map borrower requirements may mandate specific mitigation measures or insurance policies for properties located in high-risk areas. Lenders, on the other hand, use these maps to assess creditworthiness and set appropriate loan terms, including interest rates and down payment guidelines.
In regions with a history of severe flooding, such as the Midwest United States or parts of Europe, lenders often employ more stringent criteria for flood zone map borrower requirements. This includes thorough property assessments, feasibility studies, and detailed risk analyses to mitigate potential losses. Understanding these historical patterns allows investors to make informed choices, ensuring both the safety of their investments and adherence to evolving regulatory standards related to flood zone maps.
Mitigating Risk: Strategies for Safe Investment Decisions

Legal Considerations: Regulations and Insurance Implications

Navigating the complexities of investing in properties located within flood zones requires a thorough understanding of the legal framework and its direct implications on insurance. The flood zone map is a critical tool for investors, offering detailed insights into areas prone to flooding, which can significantly impact financial decisions. These maps, usually maintained by local governments or regulatory bodies, are essential resources for assessing risk and compliance.
In many jurisdictions, lenders and borrowers are mandated to consult these maps as part of the loan application process. The flood zone map borrower requirements often dictate that properties in special flood hazard areas (SFHA) require specific measures to mitigate risks before a mortgage can be approved. This includes obtaining flood insurance, which is mandatory for most loans secured by a property in a high-risk area. Lenders typically demand proof of this coverage as a condition for financing, ensuring borrowers are protected and the lender complies with regulatory obligations. For instance, according to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), over 20% of properties in the United States are located in flood zones, emphasizing the widespread relevance of these considerations.
Experts advise investors to thoroughly review the flood zone map and associated regulations before committing to any real estate transaction. Failure to comply with borrower requirements can lead to loan denials or even legal repercussions. Insurance companies also have specific criteria for properties in flood-prone areas, often assessing structural changes and improvements to determine coverage eligibility. Understanding these nuances is vital to ensure a smooth investment journey and mitigate potential financial losses.
