Flood zone maps are critical tools for real estate investors, providing visual insights into flood risks through zone designations and symbols. They range from low to high risk, with 10% of U.S. properties in high-risk zones (Special Flood Hazard Areas). Investors should consider historical flooding data, local building codes, and flood control measures. Map analysis enables strategic investment choices, managing risks, and capitalizing on opportunities while navigating regulatory requirements and compliance for responsible investing.
Investing in real estate requires a profound understanding of the territory’s unique characteristics, especially when it comes to flood zones. A detailed breakdown of the flood zone map is indispensable for investors seeking to navigate these complex areas with confidence. This article delves into the intricacies of these maps, providing a comprehensive guide to help you decipher their data and make informed decisions. By demystifying the process, we empower investors to assess risk effectively, identify opportunities, and secure investments with peace of mind, ensuring your success in even the most nuanced real estate markets.
Understanding Flood Zone Maps: A Key Tool for Investors
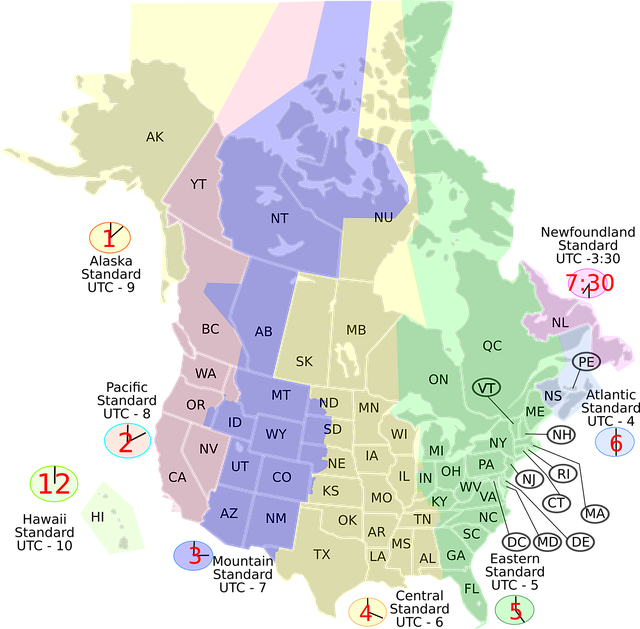
Flood zone maps are indispensable tools for investors navigating real estate markets, particularly those in areas prone to flooding. These detailed geographic representations visually communicate flood risks, offering crucial insights into areas that may be protected or vulnerable. Understanding a flood zone map is essential for informed investment decisions, as it can significantly impact property values and borrower requirements.
The process of interpreting these maps involves recognizing different zones denoted by colors or shading. Typically, they categorize areas based on their proximity to water bodies and historical flooding data. Zones may include low-risk areas, areas with a slight risk, and high-risk flood zones. For instance, in the United States, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) maps outline Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs), providing clear indications of where flooding is likely to occur. Investors should note that properties within these areas often face stricter borrower requirements from lenders concerned about elevated risk.
When evaluating investment opportunities, investors must consider not only the current flood zone classification but also historical data and climate change projections. Past flooding events can offer valuable insights into a property’s susceptibility. Additionally, understanding local building codes and infrastructure improvements related to flood control measures is vital. For example, properties in areas with improved drainage systems or levees may have lower borrower requirements compared to those without such safeguards. By thoroughly analyzing these factors, investors can make more precise decisions, mitigating potential risks while capitalizing on opportunities in diverse real estate markets.
Deciphering Map Symbols: What They Reveal About Risk

When scrutinizing a flood zone map, investors must pay meticulous attention to its symbols and markings, as these convey critical information about potential risks. Each symbol represents a specific element of the property’s flood vulnerability, offering insights that can significantly impact lending decisions. For instance, dense red areas on the map typically indicate high-risk zones prone to frequent and severe flooding, while lighter shades may represent lower-risk regions. Understanding these visual cues is paramount for investors and lenders alike, as it allows them to assess the extent of potential exposure.
Map symbols can convey a range of data, including historical flood events, predicted flood plains, and regulatory flood zones. For instance, a map might depict areas with past flooding incidents, helping investors gauge the frequency and severity of such events in that particular region. Additionally, symbols indicating regulatory flood zones—set by local authorities based on comprehensive studies—are essential for understanding legal borrower requirements. These zones dictate building restrictions, insurance obligations, and potential reimbursement policies, influencing both investment strategies and loan terms.
Deciphering these map symbols requires a deep understanding of regional hydrology and topography. For example, the presence of rivers, streams, or low-lying areas often correlates with higher flood risks. Investors should also be aware of changes in land elevation, as they can significantly impact water flow and accumulation. By integrating this visual data with other critical factors like local climate patterns and historical data, investors can make more informed decisions. This thorough analysis ensures that borrower requirements for insurance coverage and safety protocols are not only met but exceeded, fostering a robust investment strategy within clearly defined flood zone parameters.
Identifying High-Risk Areas: Locating Potential Hazards

Identifying high-risk areas is a critical step in understanding a flood zone map, particularly for investors considering property acquisitions. These maps, detailed and comprehensive, offer valuable insights into potential hazards, enabling informed decisions. By analyzing historical data on flooding events, geographic features, and topographical elements, experts can pinpoint areas prone to inundation. For instance, regions with low-lying terrain, poor drainage systems, or proximity to major water bodies are often at higher risk. Understanding these patterns is crucial for investors aiming to mitigate financial exposure and ensure the safety of future borrowers.
A thorough examination of a flood zone map reveals not only high-risk zones but also areas with varying degrees of vulnerability. This distinction is essential as it guides investors in making strategic choices. For instance, properties located within special flood hazard areas may require stricter lending standards, including higher down payments and more rigorous borrower requirements. These measures are implemented by mortgage lenders to protect against significant financial losses. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), approximately 10% of properties in the United States are considered in these high-risk zones, emphasizing the need for careful consideration.
Practical insights for investors include engaging professional appraisers and consultants who specialize in flood zone mapping. Their expertise can provide detailed reports on specific properties, offering valuable data to lenders and borrowers alike. Additionally, staying updated with local government initiatives and regulatory changes related to flood mitigation efforts is beneficial. These steps ensure that investments are not only profitable but also safe from potential catastrophic losses associated with flooding. By integrating these practices into investment strategies, investors can confidently navigate the complexities of flood zone maps while adhering to borrower requirements.
Regulatory Requirements: Compliance and Mitigation Measures

Navigating regulatory requirements when investing in areas denoted on flood zone maps is a critical aspect of responsible and successful property investment. These maps, provided by federal agencies like the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), offer essential insights into potential flood risks across various zones. Understanding these classifications—from low to high flood risk—is paramount for investors as it directly influences loan eligibility, insurance considerations, and mitigation strategies.
For instance, properties located in a Special Flood Hazard Area (SFHA), identified on the flood zone map, often face stringent borrower requirements from lenders. These requirements may include mandatory purchase of flood insurance, higher down payments, or more conservative loan-to-value ratios. According to FEMA data, over 20% of properties in high-risk zones are within SFHAs, underscoring the significance of these regulations. Investors must adhere to these guidelines not only to secure financing but also to ensure fair lending practices and mitigate potential losses for all stakeholders involved.
Compliance goes beyond loan approval. Investors should consider proactive measures to minimize flood risks, such as elevating structures or implementing flood-resistant design elements, especially in high-risk zones. These mitigation efforts can significantly reduce damage and insurance claims over time. For instance, investors in coastal areas designated on the flood zone map may opt for elevated building foundations, waterproof membranes, and robust surge protection systems to safeguard properties from recurring storms and rising sea levels.
By meticulously evaluating flood zone maps and understanding corresponding borrower requirements, investors can make informed decisions, ensure regulatory compliance, and strategically implement risk-mitigation measures. This proactive approach not only protects investments but also contributes to the overall resilience of communities, especially in light of climate change and increasingly frequent extreme weather events.
Impact on Property Values: Analyzing Market Trends

Flood zone maps are critical tools for investors navigating real estate markets, as they play a pivotal role in understanding property values and associated risks. These detailed geographic representations identify areas prone to flooding, offering essential insights into potential investments. The impact on property values is profound, with locations within designated flood zones often facing unique market trends. Investors must delve into these trends to make informed decisions, considering both the immediate effects and long-term implications.
One of the primary considerations for investors is the direct correlation between flood zone maps and property valuations. Homes or commercial spaces situated in areas identified on these maps typically command lower prices compared to those in safer zones. This disparity results from the inherent risks associated with flooding, which can lead to significant property damage and increased insurance premiums. For instance, a study analyzing post-flood market recovery in coastal cities revealed that properties in flood-prone areas took, on average, 20% longer to sell at prices 15% lower than their pre-flood values. Understanding these trends is crucial for investors aiming to maximize returns while mitigating risks.
Furthermore, lenders and mortgage underwriters often require borrowers living or investing in areas with a history of flooding to obtain detailed flood zone maps as part of the loan approval process. This requirement ensures that borrowers are fully aware of potential risks and helps lenders assess the viability of lending in these zones. According to Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) data, approximately 10% of properties in the United States are located in high-risk flood zones, with this number varying significantly by region. Investors should anticipate such borrower requirements when entering these markets, potentially influencing their strategies and investment choices.
To navigate these complexities effectively, investors are advised to consult comprehensive flood zone maps and engage with local real estate experts who can provide insights into post-flood market dynamics. By analyzing historical sales data for properties in affected areas, investors can anticipate future trends and identify potential opportunities or challenges. Staying informed about these nuances is essential, as it enables investors to make well-calculated decisions, ensuring both the preservation of assets and the realization of profitable outcomes.
Strategies for Investing in Flood Zones: Risks and Rewards
Investing in flood zones presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities for investors. A detailed examination of the flood zone map is crucial to understanding these dynamics. These maps, often provided by government agencies, offer critical insights into areas prone to flooding, enabling investors to make informed decisions. By analyzing historical data, current zoning regulations, and future development plans, investors can assess the risks and rewards associated with specific locations.
For instance, a comprehensive flood zone map borrower requirements analysis might reveal that while certain regions face frequent inundation, robust infrastructure upgrades and effective drainage systems have significantly reduced their vulnerability. Areas with such enhancements often attract developers who specialize in resilient construction methods, leading to higher-value properties and potentially lucrative investment opportunities. Conversely, zones with outdated or insufficient flood protection measures may remain at risk, necessitating caution and specialized financing strategies from borrowers.
Navigating these complexities requires a nuanced approach. Investors should engage with local experts, review historical climate data, and study the effectiveness of previous flood mitigation efforts. For instance, post-disaster recovery reports can provide valuable insights into successful adaptation strategies in high-risk areas. By integrating such knowledge into investment decisions, borrowers can mitigate risks while capitalizing on the potential for significant returns in areas that have successfully navigated or are improving their flood zone map status. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of local conditions and proactive risk management are key to thriving in these markets.
